函数评分查询
如果您需要更改结果中文档的相关性分数,请使用 function_score 查询。function_score 查询定义了一个查询和一个或多个函数,这些函数可以应用于所有结果或结果的子集以重新计算它们的相关性分数。
使用一个评分函数
最基本的 function_score 查询示例使用一个函数来重新计算分数。以下查询使用 weight 函数将所有相关性分数加倍。此函数适用于结果中的所有文档,因为在 function_score 中未指定 query 参数
GET shakespeare/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"weight": "2"
}
}
}
将评分函数应用于文档子集
要将评分函数应用于文档子集,请在该函数中提供一个查询
GET shakespeare/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": {
"play_name": "Hamlet"
}
},
"weight": "2"
}
}
}
支持的函数
function_score 查询类型支持以下函数
- 内置
weight: 将文档分数乘以预定义的提升因子。random_score: 提供一个随机分数,该分数对于单个用户是一致的,但在不同用户之间是不同的。field_value_factor: 使用指定文档字段的值重新计算分数。- 衰减函数(
gauss、exp和linear):使用指定的衰减函数重新计算分数。
- 自定义
script_score: 使用脚本对文档进行评分。
权重函数
当您使用 weight 函数时,原始相关性分数将乘以 weight 的浮点值
GET shakespeare/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"weight": "2"
}
}
}
与 boost 值不同,weight 函数未标准化。
随机评分函数
random_score 函数提供一个随机分数,该分数对于单个用户是一致的,但在不同用户之间是不同的。分数是 [0, 1) 范围内的浮点数。默认情况下,random_score 函数使用内部 Lucene 文档 ID 作为种子值,这使得随机值不可复现,因为文档在合并后可能会重新编号。为了在生成随机值时保持一致性,您可以提供 seed 和 field 参数。field 必须是启用了 fielddata 的字段(通常是数值字段)。分数是使用 seed、field 的 fielddata 值以及使用索引名称和分片 ID 计算的盐值来计算的。由于位于同一分片中的文档具有相同的索引名称和分片 ID,因此具有相同 field 值的文档将被分配相同的分数。为了确保同一分片中所有文档的分数都不同,请使用一个对所有文档都具有唯一值的 field。一种选择是使用 _seq_no 字段。但是,如果您选择此字段,则如果文档因相应的 _seq_no 更新而更改,分数也可能会更改。
以下查询使用带有 seed 和 field 的 random_score 函数
GET blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"random_score": {
"seed": 20,
"field": "_seq_no"
}
}
}
}
字段值因子函数
field_value_factor 函数使用指定文档字段的值重新计算分数。如果该字段是多值字段,则只有其第一个值用于计算,其他值不予考虑。
field_value_factor 函数支持以下选项
-
field: 用于分数计算的字段。 -
factor: 可选因子,用于将字段值乘以该因子。默认值为 1。 -
modifier: 应用于字段值 \(v\) 的修饰符之一。下表列出了所有支持的修饰符。修饰符 公式 描述 log\(\log v\) 取值的以 10 为底的对数。对非正数取对数是非法操作,将导致错误。对于 0(不含)到 1(含)之间的值,此函数返回非负值,这将导致错误。我们建议使用 log1p或log2p而不是log。log1p\(\log (1 + v)\) 取 1 与值之和的以 10 为底的对数。 log2p\(\log (2 + v)\) 取 2 与值之和的以 10 为底的对数。 ln\(\ln v\) 取值的自然对数。对非正数取对数是非法操作,将导致错误。对于 0(不含)到 1(含)之间的值,此函数返回非负值,这将导致错误。我们建议使用 ln1p或ln2p而不是ln。ln1p\(\ln (1 + v)\) 取 1 与值之和的自然对数。 ln2p\(\ln (2 + v)\) 取 2 与值之和的自然对数。 reciprocal\(\frac {1}{v}\) 取值的倒数。 square\(v^2\) 将值平方。 sqrt\(\sqrt v\) 取值的平方根。对负数取平方根是非法操作,将导致错误。确保 \(v\) 为非负数。 none不适用 不应用任何修饰符。 -
missing: 如果文档中缺少字段,则使用的值。factor和modifier将应用于此值,而不是缺少的字段值。
例如,以下查询使用 field_value_factor 函数来增加 views 字段的权重
GET blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "views",
"factor": 1.5,
"modifier": "log1p",
"missing": 1
}
}
}
}
前述查询使用以下公式计算相关性分数
\[\text{score} = \text{original score} \cdot \log(1 + 1.5 \cdot \text{views})\]脚本评分函数
使用 script_score 函数,您可以编写自定义脚本来对文档进行评分,可以选择包含文档中字段的值。原始相关性分数可在 _score 变量中访问。
计算出的分数不能为负数。负分数将导致错误。文档分数具有正的 32 位浮点值。精度更高的分数将转换为最接近的 32 位浮点数。
例如,以下查询使用 script_score 函数根据原始分数以及博客文章的浏览量和点赞数来计算分数。为了降低浏览量和点赞数的权重,此公式取浏览量和点赞数之和的对数。为了使对数即使在浏览量和点赞数为 0 时也有效,它们的和中会加上 1
GET blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {"match": {"name": "opensearch"}},
"script_score": {
"script": "_score * Math.log(1 + doc['likes'].value + doc['views'].value)"
}
}
}
}
脚本会编译和缓存以提高性能。因此,最好重用相同的脚本并传递脚本所需的任何参数
GET blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": {
"match": { "name": "opensearch" }
},
"script_score": {
"script": {
"params": {
"add": 1
},
"source": "_score * Math.log(params.add + doc['likes'].value + doc['views'].value)"
}
}
}
}
}
衰减函数
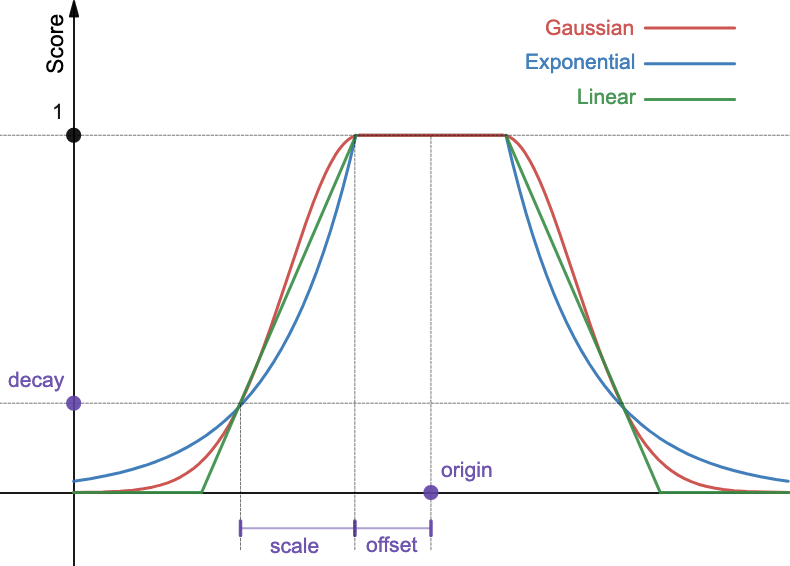
对于许多应用程序,您需要根据邻近度或新近度对结果进行排序。您可以使用衰减函数来实现此目的。衰减函数使用以下三种衰减曲线之一计算文档分数:高斯、指数或线性。
衰减函数根据origin(原点)、scale(尺度)、offset(偏移)和decay(衰减)计算分数,如下图所示。
示例:地理点字段
假设您正在寻找办公室附近的酒店。您创建一个hotels索引,将location字段映射为地理点。
PUT hotels
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
}
}
}
}
您索引两个对应附近酒店的文档。
PUT hotels/_doc/1
{
"name": "Hotel Within 200",
"location": {
"lat": 40.7105,
"lon": 74.00
}
}
PUT hotels/_doc/2
{
"name": "Hotel Outside 500",
"location": {
"lat": 40.7115,
"lon": 74.00
}
}
origin定义了计算距离的起点(办公室位置)。offset指定了文档获得满分1分的距离范围。您可以将办公室200英尺范围内的酒店赋予相同的最高分。scale定义了图表的衰减率,而decay定义了在距原点scale + offset距离处分配给文档的分数。一旦超出200英尺半径,您可能会决定,如果需要再步行300英尺才能到达酒店(scale = 300英尺),则将其分数设置为原始分数的四分之一(decay = 0.25)。
您创建以下查询,将origin设置为(74.00, 40.71)。
GET hotels/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"functions": [
{
"exp": {
"location": {
"origin": "40.71,74.00",
"offset": "200ft",
"scale": "300ft",
"decay": 0.25
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
响应包含两家酒店。办公室200英尺范围内的酒店得分为1,而超出500英尺半径的酒店得分为0.20,低于decay参数0.25。
响应
{
"took": 854,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 2,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "hotels",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Hotel Within 200",
"location": {
"lat": 40.7105,
"lon": 74
}
}
},
{
"_index": "hotels",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 0.20099315,
"_source": {
"name": "Hotel Outside 500",
"location": {
"lat": 40.7115,
"lon": 74
}
}
}
]
}
}
参数
下表列出了gauss、exp和linear函数支持的所有参数。
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
origin | 计算距离的起点。对于数字字段,必须提供一个数字;对于日期字段,必须提供一个日期;对于地理点字段,必须提供一个地理点。对于地理点和数字字段为必填项。对于日期字段为可选项(默认为now)。对于日期字段,支持日期运算(例如,now-2d)。 |
offset | 定义了文档在距原点多少距离内获得分数1。可选。默认为0。 |
scale | 距离origin scale + offset的文档将被分配decay分数。必填。对于数字字段, scale可以是任何数字。对于日期字段, scale可以定义为带单位的数字(5h, 1d)。如果未提供单位,scale默认为毫秒。对于地理点字段, scale可以定义为带单位的数字(1mi, 5km)。如果未提供单位,scale默认为米。 |
decay | 定义了文档在距origin scale + offset距离处的分数。可选。默认为0.5。 |
对于文档中缺失的字段,衰减函数返回分数1。
示例:数字字段
以下查询使用指数衰减函数根据评论数量对博客文章进行优先级排序。
GET blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"functions": [
{
"exp": {
"comments": {
"origin": "20",
"offset": "5",
"scale": "10"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
结果中的前两篇博客文章得分为1,因为一篇在原点(20),另一篇距离为16,在偏移范围内(文档获得满分的范围计算为20 \(\pm\) 5,即[15, 25])。第三篇博客文章距离origin的距离为scale + offset(20 − (5 + 10) = 15),因此它获得默认的decay分数(0.5)。
响应
{
"took": 3,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 4,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Semantic search in OpenSearch",
"views": 1200,
"likes": 150,
"comments": 16,
"date_posted": "2022-04-17"
}
},
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Get started with OpenSearch 2.7",
"views": 1400,
"likes": 100,
"comments": 20,
"date_posted": "2022-05-02"
}
},
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 0.5,
"_source": {
"name": "Distributed tracing with Data Prepper",
"views": 800,
"likes": 50,
"comments": 5,
"date_posted": "2022-04-25"
}
},
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0.4352753,
"_source": {
"name": "A very old blog",
"views": 100,
"likes": 20,
"comments": 3,
"date_posted": "2000-04-25"
}
}
]
}
}
示例:日期字段
以下查询使用高斯衰减函数,优先显示2002年4月24日左右发布的博客文章。
GET blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"functions": [
{
"gauss": {
"date_posted": {
"origin": "2022-04-24",
"offset": "1d",
"scale": "6d",
"decay": 0.25
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
在结果中,第一篇博客文章发布于2022年4月24日的一天之内,因此它的分数为最高分1。第二篇博客文章发布于2022年4月17日,这在offset + scale(1d + 6d)之内,因此其分数等于decay(0.25)。第三篇博客文章发布于2022年4月24日之后超过7天,因此其分数较低。最后一篇博客文章得分为0,因为它是在几年前发布的。
响应
{
"took": 2,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 4,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"name": "Distributed tracing with Data Prepper",
"views": 800,
"likes": 50,
"comments": 5,
"date_posted": "2022-04-25"
}
},
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 0.25,
"_source": {
"name": "Semantic search in OpenSearch",
"views": 1200,
"likes": 150,
"comments": 16,
"date_posted": "2022-04-17"
}
},
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 0.15154076,
"_source": {
"name": "Get started with OpenSearch 2.7",
"views": 1400,
"likes": 100,
"comments": 20,
"date_posted": "2022-05-02"
}
},
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "4",
"_score": 0,
"_source": {
"name": "A very old blog",
"views": 100,
"likes": 20,
"comments": 3,
"date_posted": "2000-04-25"
}
}
]
}
}
多值字段
如果用于衰减计算的字段包含多个值,您可以使用multi_value_mode参数。此参数指定以下函数之一来确定用于计算的字段值:
min:(默认)距origin的最小距离。max:距origin的最大距离。avg:距origin的平均距离。sum:距origin的所有距离之和。
例如,您索引一个包含距离数组的文档:
PUT testindex/_doc/1
{
"distances": [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
以下查询使用多值字段distances的max距离来计算衰减:
GET testindex/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"functions": [
{
"exp": {
"distances": {
"origin": "6",
"offset": "5",
"scale": "1"
},
"multi_value_mode": "max"
}
}
]
}
}
}
该文档得分为1,因为距原点的最大距离(1)在距origin的offset之内。
{
"took": 3,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 1,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "testindex",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 1,
"_source": {
"distances": [
1,
2,
3,
4,
5
]
}
}
]
}
}
衰减曲线计算
以下公式定义了各种衰减函数的分数计算(\(v\)表示文档字段值)。
高斯
\[\text{score} = \exp \left(-\frac {(\max(0, \lvert v - \text{origin} \rvert - \text{offset}))^2} {2\sigma^2} \right),\]其中\(\sigma\)的计算是为了确保在距origin offset + scale的距离处,分数值等于decay。
指数
\[\text{score} = \exp (\lambda \cdot \max(0, \lvert v - \text{origin} \rvert - \text{offset})),\]其中\(\lambda\)的计算是为了确保在距origin offset + scale的距离处,分数值等于decay。
线性
\[\text{score} = \max \left(\frac {s - \max(0, \lvert v - \text{origin} \rvert - \text{offset})} {s} \right),\]其中\(s\)的计算是为了确保在距origin offset + scale的距离处,分数值等于decay。
使用多个评分函数
您可以通过在functions数组中列出多个评分函数,在一个函数评分查询中指定它们。
组合来自多个函数的分数
不同的函数可以使用不同的评分尺度。例如,random_score函数提供0到1之间的分数,但field_value_factor没有特定的分数尺度。此外,您可能希望对不同函数给出的分数进行不同的加权。为了调整不同函数的分数,您可以为每个函数指定weight参数。每个函数给出的分数随后乘以weight,以产生该函数的最终分数。weight参数必须在functions数组中提供,以区别于权重函数。
每个函数给出的分数通过score_mode参数进行组合,该参数取以下值之一:
multiply:(默认)分数相乘。sum:分数相加。avg:分数取平均值。如果指定了weight,则为加权平均值。例如,如果第一个权重为\(1\)的函数返回分数\(10\),第二个权重为\(4\)的函数返回分数\(20\),则平均值计算为\(\frac {10 \cdot 1 + 20 \cdot 4}{1 + 4} = 18\)。first:取第一个具有匹配过滤器的函数的分数。max:取最高分数。min:取最低分数。
指定分数的上限
您可以在max_boost参数中为函数分数指定一个上限。默认上限是float值的最大幅度:(2 − 2−23) · 2127。
将所有函数的分数与查询分数结合
您可以在boost_mode参数中指定如何将所有函数计算的分数与查询分数结合,该参数取以下值之一:
multiply:(默认)查询分数乘以函数分数。replace:忽略查询分数,使用函数分数。sum:查询分数与函数分数相加。avg:查询分数与函数分数取平均值。max:取查询分数和函数分数中较大者。min:取查询分数和函数分数中较小者。
过滤不符合阈值的文档
更改相关性分数不会改变匹配文档的列表。要排除一些不符合阈值的文档,请在min_score参数中指定阈值。查询返回的所有文档随后将使用该阈值进行评分和过滤。
示例
以下请求搜索包含“OpenSearch Data Prepper”字样的博客文章,优先显示2022年4月24日左右发布的文章。此外,还会考虑浏览量和点赞数。最后,截止阈值设置为10分。
GET blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"boost": "5",
"functions": [
{
"gauss": {
"date_posted": {
"origin": "2022-04-24",
"offset": "1d",
"scale": "6d"
}
},
"weight": 1
},
{
"gauss": {
"likes": {
"origin": 200,
"scale": 200
}
},
"weight": 4
},
{
"gauss": {
"views": {
"origin": 1000,
"scale": 800
}
},
"weight": 2
}
],
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "opensearch data prepper"
}
},
"max_boost": 10,
"score_mode": "max",
"boost_mode": "multiply",
"min_score": 10
}
}
}
结果包含三篇匹配的博客文章。
响应
{
"took": 14,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 31.191923,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "3",
"_score": 31.191923,
"_source": {
"name": "Distributed tracing with Data Prepper",
"views": 800,
"likes": 50,
"comments": 5,
"date_posted": "2022-04-25"
}
},
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 13.907352,
"_source": {
"name": "Semantic search in OpenSearch",
"views": 1200,
"likes": 150,
"comments": 16,
"date_posted": "2022-04-17"
}
},
{
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "2",
"_score": 11.150461,
"_source": {
"name": "Get started with OpenSearch 2.7",
"views": 1400,
"likes": 100,
"comments": 20,
"date_posted": "2022-05-02"
}
}
]
}
}
命名函数
在定义函数时,您可以在顶级使用_name参数指定其名称。此名称对于调试和理解评分过程很有用。一旦指定,函数名称将尽可能地包含在分数计算解释中(这适用于函数、过滤器和查询)。您可以通过响应中的_name来识别该函数。
示例
以下请求将explain设置为true用于调试,以便在响应中获取评分解释。每个函数都包含一个_name参数,以便您可以明确识别该函数。
GET blogs/_search
{
"explain": true,
"size": 1,
"query": {
"function_score": {
"functions": [
{
"_name": "likes_function",
"script_score": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "return doc['likes'].value * 2;"
}
},
"weight": 0.6
},
{
"_name": "views_function",
"field_value_factor": {
"field": "views",
"factor": 1.5,
"modifier": "log1p",
"missing": 1
},
"weight": 0.3
},
{
"_name": "comments_function",
"gauss": {
"comments": {
"origin": 1000,
"scale": 800
}
},
"weight": 0.1
}
]
}
}
}
响应解释了评分过程。对于每个函数,解释在其description中包含函数_name。
响应
{
"took": 14,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": {
"value": 3,
"relation": "eq"
},
"max_score": 6.1600614,
"hits": [
{
"_shard": "[blogs][0]",
"_node": "_yndTaZHQWimcDgAfOfRtQ",
"_index": "blogs",
"_id": "1",
"_score": 6.1600614,
"_source": {
"name": "Semantic search in OpenSearch",
"views": 1200,
"likes": 150,
"comments": 16,
"date_posted": "2022-04-17"
},
"_explanation": {
"value": 6.1600614,
"description": "function score, product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 1,
"description": "*:*",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 6.1600614,
"description": "min of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 6.1600614,
"description": "function score, score mode [multiply]",
"details": [
{
"value": 180,
"description": "product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 300,
"description": "script score function(_name: likes_function), computed with script:\"Script{type=inline, lang='painless', idOrCode='return doc['likes'].value * 2;', options={}, params={}}\"",
"details": [
{
"value": 1,
"description": "_score: ",
"details": [
{
"value": 1,
"description": "*:*",
"details": []
}
]
}
]
},
{
"value": 0.6,
"description": "weight",
"details": []
}
]
},
{
"value": 0.9766541,
"description": "product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 3.2555137,
"description": "field value function(_name: views_function): log1p(doc['views'].value?:1.0 * factor=1.5)",
"details": []
},
{
"value": 0.3,
"description": "weight",
"details": []
}
]
},
{
"value": 0.035040613,
"description": "product of:",
"details": [
{
"value": 0.35040614,
"description": "Function for field comments:",
"details": [
{
"value": 0.35040614,
"description": "exp(-0.5*pow(MIN[Math.max(Math.abs(16.0(=doc value) - 1000.0(=origin))) - 0.0(=offset), 0)],2.0)/461662.4130844683, _name: comments_function)",
"details": []
}
]
},
{
"value": 0.1,
"description": "weight",
"details": []
}
]
}
]
},
{
"value": 3.4028235e+38,
"description": "maxBoost",
"details": []
}
]
}
]
}
}
]
}
}